Angioplasty and stent placement - carotid artery
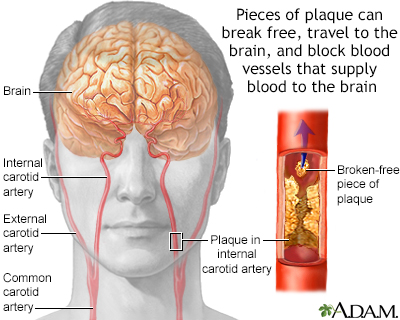
Carotid angioplasty and stenting; CAS; Angioplasty - carotid artery; Carotid artery stenosis - angioplastyThe blood vessels that bring blood to your brain and face are called the carotid arteries. You have a carotid artery on each side of your neck.
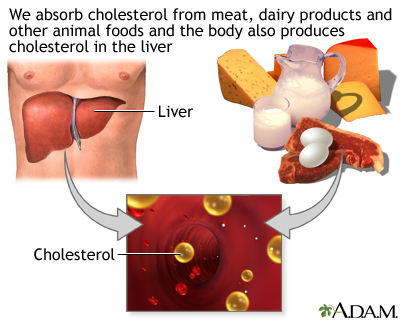
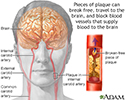
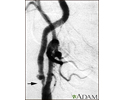
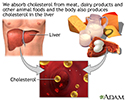
The blood flow in this artery can become partly or totally blocked by fatty material called plaque. A partial blockage is called carotid artery stenosis (narrowing). A blockage in your carotid artery can reduce the blood supply to your brain. Sometimes part of a plaque can break off, travel downstream and block a brain artery. A stroke can occur if your brain does not get enough blood.
Two procedures can be used to treat a carotid artery that is narrowed or blocked. These are:
- Surgery to remove plaque buildup (endarterectomy)
- Carotid artery angioplasty with stent placement
Description
Carotid artery angioplasty and stenting (CAS) is done using a small surgical cut.
- Your health care provider will make a surgical cut in your groin after using some numbing medicine. You will also be given medicine to relax you.
- The provider places a catheter (a flexible tube) through the cut into an artery. It is carefully moved up to your neck to the blockage in your carotid artery. Moving x-ray pictures (fluoroscopy) are used to see the artery and guide the catheter to the correct position.
- Next, the provider will move a wire through the catheter to the blockage. Another catheter with a very small balloon on the end will be pushed over this wire and into the blockage. Then the balloon is inflated.
- The balloon presses against the inside wall of your artery. This opens the artery and allows more blood to flow to your brain. A stent (a wire mesh tube) may also be placed in the blocked area. The stent is inserted at the same time as the balloon catheter. It expands with the balloon. The stent is left in place to help keep the artery open.
- The provider then removes the balloon and catheters.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Carotid artery surgery (endarterectomy) is a well-established and effective way to treat narrowed or blocked arteries. This procedure is very safe.
CAS has developed as a good alternative to surgery in some cases, when done by experienced providers. Certain factors may favor stenting, such as:
- The person is too ill to have carotid endarterectomy.
- The location of the narrowing in the carotid artery makes surgery harder.
- The person has had neck or carotid surgery in the past.
- The person has had radiation to the neck.
Risks
Risks of CAS, which depend on factors such as age, are:
- Allergic reaction to dye
- Blood clots or bleeding at the site of surgery
- Brain damage
- Clogging of the inside of the stent (in-stent restenosis)
- Heart attack
- Kidney failure (higher risk in people who already have kidney problems)
- More blockage of the carotid artery over time
- Seizures (this is rare)
- Stroke
Before the Procedure
Your provider will do a physical exam and perform several medical tests.
Tell your provider or nurse if:
- You are taking any medicines, including medicines, drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription
During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your provider which medicines you should still take on the day of surgery.
- On the day of the procedure:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your provider told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
Always tell your provider what medicines you are taking, including drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription.
After the Procedure
After the procedure, you may need to stay in the hospital overnight so that you can be watched for any signs of bleeding, stroke, or poor blood flow to your brain. You may be able to go home the same day if your procedure is done early in the day and you are doing well. Your provider will talk to you about how to care for yourself at home.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Carotid artery angioplasty and stenting may help lower your chance of having a stroke. But you may need to make lifestyle changes, such as change in diet and regular exercise, to help prevent plaque buildup, blood clots, and other problems in your carotid arteries over time. In addition, your provider will recommend medicines to further reduce your chance of a stroke.
References
AbuRahma AF, Avgerinos ED, Chang RW, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery clinical practice guidelines for management of extracranial cerebrovascular disease. J Vasc Surg. 2022;75(1S):4S-22S. PMID: 34153348 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34153348/.
Deery SE, Hicks CW. Carotid artery stenting. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 94.
Kinlay S, Bhatt DL. Treatment of noncoronary obstructive vascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 44.
Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, et al. 2021 guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: A guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021;52(7):e364-e467. PMID: 34024117 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34024117/.
Rogers RK, Seinfeld J, Casserly IP. Carotid and cerebrovascular intervention. In: Topol EJ, Teirstein PS, eds. Textbook of Interventional Cardiology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 46.